Chile’s Copper Boom: How Global Demand Drives Chile’s Mining Success
Overview of Chile’s Copper Boom in Chile
In recent years, Chile has emerged as a global powerhouse in the mining industry, primarily due to its abundant copper reserves. The country’s success in copper production has led to a significant economic boom, cementing its position as one of the world’s leading copper producers. As the demand for copper continues to rise in various industries, Chile’s mining sector plays a crucial role in meeting global needs.
Significance of Copper in the Global Economy
Copper holds a unique position in the global economy due to its diverse applications across numerous sectors. Often referred to as “Dr. Copper,” it is considered an excellent barometer of economic health because of its widespread use in construction, electronics, transportation, and renewable energy systems. As a highly conductive metal, copper is an essential component in electrical wiring and plays a fundamental role in facilitating power transmission and distribution.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, has further increased the demand for copper, as it is an indispensable element in manufacturing solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems. Additionally, the rapid expansion of urban centers and infrastructure development in emerging economies has driven the demand for copper-based products, making it an essential commodity for global progress.
The Rich Copper Reserves of Chile
Introduction to Chile’s Geological Advantage
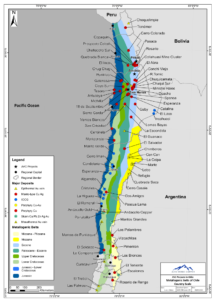
Chile’s geological landscape has bestowed upon it a bountiful endowment of copper reserves. The country’s unique tectonic setting, characterized by the convergence of the Nazca and South American plates, has played a significant role in the formation of these valuable deposits. Over millions of years, the subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South American Plate has led to the creation of vast volcanic arcs and mineral-rich zones, fostering the accumulation of copper deposits in various regions of Chile.
Major Copper Deposits in Chile
Chile boasts an impressive array of copper deposits, each contributing to its status as a copper mining powerhouse. Some of the most notable copper deposits in the country include:
- Chuquicamata: Located in the northern region of Antofagasta, Chuquicamata is one of the world’s largest open-pit copper mines. It has been in operation since the early 20th century and continues to be a significant source of copper production.
- Escondida: Situated in the Atacama Desert, Escondida is the world’s largest copper mine by production. It is operated as an open-pit mine and has been a critical contributor to Chile’s copper output for several decades.
- Collahuasi: Located in northern Chile, Collahuasi is one of the largest copper mines in terms of reserves. It is a joint venture between two major mining companies and has been a major player in Chile’s copper industry.
- El Teniente: Situated in central Chile, El Teniente is one of the world’s deepest underground copper mines. It has a long history of copper production and remains a vital asset in Chile’s mining portfolio.
“The geological setting in Chile is unparalleled in its mineral endowment. This has spawned a very strong mining industry which remains one of Chile’s largest contributors to the national economy. At the forefront of this industry is the production of copper, and the associated exploration for it. As the largest copper producer in the world, Chile hosts many notable copper miners, including Antofagasta Minerals, BHP Billiton, Glencore, Freeport-McMoRan and Codelco among others, and there has been significant exploration and production in the region for decades. With its well-developed sector, Chile is also known as a highly favourable mining jurisdiction within South America, with a long history of strong mining laws supporting foreign direct investment.” – Stephan Bogner, Rockstone Research
Comparison of Chile’s Copper Reserves with Other Countries
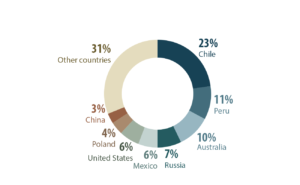
Chile’s copper reserves are among the largest globally, accounting for a significant portion of the world’s total copper resource. The country’s abundance of high-grade copper ore has given it a competitive advantage in the global mining landscape. When compared to other copper-producing nations, Chile consistently ranks at the top in terms of production and reserves.
This geological advantage, combined with sound mining practices and a favorable business environment, has positioned Chile as a reliable and leading supplier of copper to the global market. As a result, the country’s copper reserves have played a pivotal role in driving its mining success and economic growth.
World reserves of copper, by country, 2021
The Role of Copper in the Global Economy
Copper’s indispensability extends to a wide array of industries, making it a crucial metal in the global economy. Its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal properties, malleability, and corrosion resistance have made it an essential material in the following sectors:
- Electrical and Electronics: The electrical industry heavily relies on copper for wiring, power generation, and transmission. From household wiring to high-voltage power lines and transformers, copper’s low resistance and high conductivity ensure efficient electricity flow. Additionally, copper is extensively used in electronic devices, including smartphones, computers, and other gadgets.
- Construction and Infrastructure: Copper is a key component in the construction industry, used in plumbing, roofing, heating, and cooling systems. Its durability and resistance to corrosion make it ideal for long-lasting infrastructure projects like bridges, buildings, and transportation networks.
- Transportation: Copper plays a critical role in various transportation modes, including automobiles, trains, and aircraft. It is used in electrical components, motors, and connectors, contributing to the efficiency and safety of modern transportation systems.
- Renewable Energy: With the global shift towards renewable energy sources, copper’s significance has grown even further. Solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems rely heavily on copper wiring and components, driving the demand for the metal.
Visualizing the Copper Intensity of Renewable Energy
Copper as an Economic Indicator
Copper has earned the moniker “Dr. Copper” due to its ability to act as an economic bellwether. The metal’s demand and pricing trends are closely correlated with the overall health of the global economy. As copper consumption increases during periods of economic growth, its prices tend to rise. Conversely, during economic downturns, reduced demand for copper often signifies a slowdown in economic activity.
This sensitivity to economic conditions makes copper a valuable tool for analysts and policymakers to gauge economic sentiment and potential trends. It provides insights into industrial production, construction activities, and overall business confidence, offering a macroeconomic perspective on global economic health.
Understanding Global Copper Demand
In recent years, the demand for copper has surged, driven by several factors:
- Urbanization and Infrastructure Development: Rapid urbanization and infrastructure projects in emerging economies have led to a substantial demand for copper-based products. As cities expand and modernize, the need for copper in buildings, transportation systems, and energy infrastructure intensifies.
- Renewable Energy Growth: The global transition to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, has increased the demand for copper in the manufacturing of solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems.
- Technological Advancements: The ongoing technological advancements in electronics and telecommunications have escalated the demand for copper in consumer electronics and communication devices.
- Economic Growth in Emerging Markets: The growth of emerging economies, particularly in Asia, has created a surge in copper demand, driven by increased industrial production and infrastructure development.
The interplay between global copper demand and Chile’s mining success will be further explored in the subsequent sections. Understanding the significance of copper in the global economy will help us comprehend the pivotal role that Chile’s mining industry plays in meeting this ever-growing demand.
“We believe Copper has a long way to run, from where we are at currently” – CEO of Interra Copper, Chris Buncic
Chile’s Dominance in Copper Production
Historical Background of Chilean Copper Mining
Chile’s association with copper dates back centuries, with evidence of copper mining by indigenous peoples long before the arrival of the Spanish colonizers. However, it was during the 19th and 20th centuries that Chile’s copper industry experienced significant growth and development. The introduction of modern mining techniques and the discovery of large copper deposits propelled the country into becoming a major copper producer.
In the early 20th century, the opening of large-scale copper mines, such as Chuquicamata and El Teniente, marked a turning point for Chile’s copper industry. These mines, known for their vast mineral wealth, provided a substantial boost to the country’s economy and laid the foundation for its current dominance in copper production.
Key Factors Behind Chile’s Mining Success
Chile’s position as a leading copper producer is attributed to several key factors that have contributed to its mining success:
- Political Stability and Favorable Mining Policies: Chile has maintained a stable political environment, fostering investor confidence and encouraging long-term investments in the mining sector. The government’s commitment to maintaining a favorable mining policy, which includes clear regulations and support for foreign direct investment, has further attracted mining companies to operate in Chile.
- Technological Advancements in Mining Processes: The Chilean mining industry has embraced technological innovations to improve operational efficiency and reduce costs. Advanced mining methods, including open-pit and underground mining techniques, have enabled more effective extraction of copper ore from deep within the earth.
- Skilled Workforce and Training: Chile boasts a skilled and experienced mining workforce that has been instrumental in maximizing productivity and maintaining safety standards. The government and mining companies have also invested in training programs to continually improve the expertise of the workforce.
- Investment in Infrastructure and Logistics: Recognizing the importance of efficient transportation and logistics, Chile has made significant investments in developing infrastructure to support the mining sector. Well-developed roads, ports, and railways facilitate the transportation of copper from mines to international markets.
Comparative Analysis of Chile’s Production vs. Other Copper Producers
Chile’s prominence in the copper industry becomes evident when comparing its production with other major copper-producing countries. With its vast copper reserves, advanced mining practices, and supportive policies, Chile consistently ranks as one of the top copper producers in the world. Its ability to meet the growing global demand for copper has solidified its position as a reliable supplier in the international market.
While other countries also contribute significantly to global copper production, Chile’s competitive advantage lies in the sheer scale and quality of its copper reserves. This dominance has allowed Chile to play a pivotal role in influencing copper prices and shaping the dynamics of the global copper market.
Global Demand Drivers for Copper
The Growing Role of Copper in Renewable Energy
As the world transitions toward sustainable energy sources, copper’s importance in renewable energy technologies cannot be overstated. Solar and wind power, in particular, heavily rely on copper due to its excellent electrical conductivity and durability. Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels use copper wiring to efficiently transfer electricity, while wind turbines utilize copper in their generators and power distribution systems.
The increasing adoption of solar and wind energy projects worldwide has driven the demand for copper. As countries seek to reduce their carbon footprint and shift away from fossil fuels, the need for copper-intensive renewable energy infrastructure is expected to continue growing.
Visualizing Copper’s Role in the Transition to Clean Energy
Urbanization and Infrastructure Development
Global urbanization and infrastructure development have significantly contributed to the demand for copper. As populations concentrate in urban centers, the construction of buildings, transportation networks, and utility systems has surged. Copper’s reliability, durability, and ability to withstand extreme weather conditions make it an ideal choice for electrical wiring, plumbing, and various infrastructure components.
The ongoing development of smart cities, with their emphasis on efficient energy distribution and advanced communication networks, further fuels the demand for copper-based technologies. These trends underscore the pivotal role that Chile’s copper production plays in supporting worldwide urbanization efforts.
Technology and Electronics Industry’s Dependence on Copper
The booming technology and electronics sector is another major driver of copper demand. Copper is a fundamental component in electronic devices, ranging from smartphones and computers to tablets and appliances. The miniaturization of electronic components has led to higher copper usage per device, further intensifying the demand.
As technological advancements continue to shape modern society, the demand for copper in the electronics industry is expected to remain robust. Chile’s mining success assumes greater significance in meeting this demand and supporting the growth of global technology-driven economies.
Emerging Economies and Their Impact on Copper Demand
The rapid growth of emerging economies, particularly in Asia, has been a significant factor in driving global copper demand. As these countries industrialize and experience increased urbanization, the need for copper in infrastructure development, manufacturing, and energy generation escalates.
China, in particular, has become the world’s largest consumer of copper, with its expanding industrial and construction sectors being major contributors to copper consumption. Chile’s strategic position in supplying copper to emerging markets has strengthened its role as a key player in meeting the needs of these fast-growing economies.
The interplay between global demand drivers and Chile’s mining prowess has had a profound impact on the country’s economic prosperity. However, this success has not been without challenges. In the following section, we will examine the hurdles faced by Chile’s copper industry, particularly in terms of environmental sustainability and the well-being of local communities.
Challenges Faced by Chile’s Copper Industry
Environmental Concerns and Sustainability Initiatives
The rapid expansion of Chile’s copper mining industry has raised environmental concerns regarding the impact of mining activities on ecosystems and natural resources. Extracting and processing copper ore can lead to deforestation, water pollution, soil degradation, and habitat destruction, affecting local flora and fauna. Additionally, the extensive use of water in mining operations can strain local water supplies, especially in regions already facing water scarcity.
In response to these environmental challenges, the Chilean government and mining companies have been increasingly focusing on sustainability initiatives. Efforts are being made to adopt cleaner and more efficient mining practices that minimize environmental harm. Implementing water recycling and treatment technologies, reclaiming mined lands, and developing biodiversity conservation plans are among the measures taken to mitigate the ecological footprint of copper mining.
Socioeconomic Impact on Local Communities
While Chile’s mining success has contributed significantly to its economic growth, it has also presented socioeconomic challenges for local communities. The influx of mining operations often brings an influx of temporary workers from outside the region, affecting the local labor market and potentially displacing traditional livelihoods. Moreover, the rapid growth of mining towns can strain social services and infrastructure, leading to uneven development and socioeconomic disparities.
To address these issues, mining companies are working towards enhancing community engagement and promoting local employment. Investing in social programs, education, and healthcare facilities has become a priority to ensure that mining activities positively impact the well-being of nearby communities.
Competing with Other Copper Producers
As the global demand for copper rises, Chile faces increasing competition from other copper-producing countries. Nations such as Peru, China, the United States, and the Democratic Republic of Congo also possess significant copper reserves and have been ramping up their production.
Maintaining a competitive edge in the global copper market requires continuous efforts to optimize mining processes, improve infrastructure, and invest in research and development to enhance productivity. Additionally, geopolitical factors, international trade policies, and fluctuations in copper prices can also influence Chile’s position as a leading copper producer.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for sustaining Chile’s mining success in the long run. By adopting sustainable practices, prioritizing community development, and remaining adaptable in a dynamic global market, Chile’s copper industry can navigate these obstacles and continue to thrive.
In the next section, we will look into the future of Chile’s copper boom, analyzing the projected global demand for copper and the measures Chile is taking to meet this demand sustainably.
The Future of Chile’s Copper Boom
Projected Global Demand for Copper
The future outlook for copper remains optimistic, with continued strong demand anticipated across various industries. The increasing transition to renewable energy sources, coupled with ongoing urbanization and infrastructure development in emerging economies, will drive the need for copper-based products.
The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is also expected to significantly impact copper demand. Electric vehicles require a higher amount of copper compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles due to their electric motors and batteries. As more countries and manufacturers commit to the electrification of transportation, the demand for copper in the automotive sector is projected to surge.
Moreover, the electrification of industries, such as construction machinery and industrial equipment, is also likely to contribute to copper demand growth. Smart grid technologies and energy storage solutions will further add to the metal’s importance in facilitating energy distribution and management.
Chile’s Efforts in Meeting Future Demand
Chile recognizes the opportunities and challenges presented by the projected global demand for copper. To ensure its mining success in the face of growing requirements, the country is taking proactive measures:
- Sustainable Mining Practices: Chile is investing in sustainable mining practices to minimize the environmental impact of copper extraction. Emphasis on reducing water usage, implementing efficient waste management, and adopting cleaner technologies will remain a priority to ensure responsible mining operations.
- Technological Advancements: The Chilean mining industry continues to embrace technological innovations to enhance productivity and efficiency. The adoption of automation, data analytics, and remote monitoring systems will play a crucial role in optimizing mining processes.
- Diversification of Exports: Chile is actively exploring new markets and diversifying its copper exports to reduce dependency on specific countries. By reaching out to emerging economies and forging new trade partnerships, Chile aims to secure stable markets for its copper products.
- Social and Community Development: To address the social challenges associated with mining, Chile is committed to fostering positive community relations. Investing in education, healthcare, and local infrastructure ensures that the benefits of mining extend to nearby communities.
Additionally, brand-new Chilean Copper projects in Chile. are in full motion to get up and running to help meet the demand. These small scale projects are a very important for the future copper production growth as the currently producing projects slowly run out of resources. ” We all have this similar thinking that copper is at the beginning of a great new bull run. So, we wanted to form a new Copper company” – Chris Buncic, CEO of Interra Copper
Sustainable Practices for Long-Term Success
As the world becomes more focused on sustainability, Chile’s copper industry is increasingly aligning its strategies with responsible practices. Sustainability certifications, adherence to international environmental standards, and transparent reporting have become integral to maintaining a positive global reputation.
Chile’s mining success in the future will hinge on striking a balance between meeting the world’s copper demands and preserving its natural environment. By embracing sustainable practices and prioritizing the well-being of local communities, Chile can continue to be a key player in the global copper market for generations to come.
Final Overview
The copper boom in Chile stands as a remarkable testament to the nation’s geological wealth and its proactive approach to meeting global demand for this essential metal. From its historical roots to the present-day, Chile’s mining success has played a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s economy and contributing significantly to the global copper market.
The significance of copper in the global economy cannot be overstated. Its diverse applications across various industries, including electronics, renewable energy, construction, and transportation, have solidified its position as a critical commodity and an economic indicator. As the world transitions towards sustainability and embraces green technologies, the demand for copper is expected to surge even further, providing Chile with immense opportunities and challenges.
Chile’s dominance in copper production can be attributed to several key factors. The nation’s political stability, favorable mining policies, technological advancements, and skilled workforce have all contributed to its mining success. Additionally, Chile’s abundant copper reserves and efficient infrastructure have positioned it as a reliable supplier in the global market.
However, with success come responsibilities. Chile faces environmental challenges and the need to ensure the sustainable development of its mining industry. Environmental concerns, such as habitat destruction and water pollution, necessitate the adoption of sustainable mining practices and the implementation of eco-friendly technologies.
Furthermore, the socioeconomic impact on local communities demands a concerted effort to support community development, provide job opportunities, and address the needs of those affected by mining activities.
Looking ahead, Chile’s proactive measures to address these challenges bode well for the future of its copper boom. As global demand for copper continues to rise, the nation’s commitment to sustainability, technological advancements, and diversification of export markets will be crucial for maintaining its position as a leading copper producer.
The interplay between Chile’s mining success and the world’s evolving needs for copper is an ongoing story. As the nation navigates the complexities of a dynamic global market, the focus on responsible mining practices and community well-being will be instrumental in shaping the future of Chile’s copper industry.
The copper boom in Chile exemplifies the symbiotic relationship between geological advantages, economic opportunities, and sustainable practices. As the world’s demand for copper evolves, Chile’s continued commitment to responsible mining and community development will ensure that the country remains a key player in the global copper market, contributing to the progress of the global economy while preserving its natural resources for generations to come.
References
- World Bank. (2020). Copper. Commodity Markets Outlook, April 2020. Retrieved from https://www.worldbank.org/en/research/commodity-markets
- Sillitoe, R. H. (2010). Porphyry copper systems. Economic Geology, 105(1), 3-41. DOI: 10.2113/gsecongeo.105.1.3
- Mutschler, F. E., & Verhaeghe, M. (2015). Chilean copper porphyries – A compilation. Society of Economic Geologists Special Publication, 19, 139-176.
- Ang, B. W., & Choong, W. L. (2011). Impact of sectoral energy and labor productivity changes on the growth of world economies. Energy Economics, 33(3), 412-424. DOI: 10.1016/j.eneco.2010.12.004
- International Copper Study Group. (2020). Copper Market Forecast 2020-2021. Retrieved from https://www.icsg.org/publications/forecast/2020-2021.pdf
- Campbell, C., & Yang, Y. (2018). Chile’s copper production and exports: from the twentieth century to the twenty-first century. Resources Policy, 57, 52-61. DOI: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2018.01.002
- Johnson, D. A., & Oliver, N. H. S. (2016). Chilean copper mining costs. Wood Mackenzie, 10, 1-7.
- International Energy Agency. (2020). Renewable Energy Market Update. Retrieved from https://www.iea.org/reports/renewable-energy-market-update
- European Copper Institute. (2021). Copper in the EV industry. Retrieved from https://copperalliance.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Copper-in-the-EV-Industry-March-2021.pdf
- UNEP. (2017). Environmental Impacts of the Chilean Copper Mining Boom: Civil Society and the Environment in a Contested Political Economy. Retrieved from https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/19492/ChileanCopperMiningBoom.pdf
- World Bank Group. (2020). The social and economic impact of COVID-19 in Chile: Understanding the inequalities. Retrieved from https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/34848
- Reardon, S., Timilsina, G. R., & Moomaw, W. (2020). The Effect of Renewable Energy Development on Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Energies, 13(3), 740. DOI: 10.3390/en13030740
- Allcott, H., & Greenstone, M. (2012). Is There an Energy Efficiency Gap? Journal of Economic Perspectives, 26(1), 3-28. DOI: 10.1257/jep.26.1.3
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). (2020). Commodities at a glance: Special issue on copper. Retrieved from https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/ditccom2019d4_en.pdf
- International Copper Study Group. (2022). Copper Supply & Usage 2021 Preliminary Data. Retrieved from https://www.icsg.org/publications/supply-and-usage-reports/2021-2/copper-supply-usage-2021-preliminary-data
—
Disclaimer: This article, along with any associated content, contains forward-looking information or forward-looking statements (collectively “forward-looking information”) within the meaning of applicable securities laws. Such forward-looking information is typically identified by terms such as: “believe”, “expect”, “anticipate”, “intend”, “estimate”, “potentially”, and similar expressions, or statements that events or conditions “may”, “will”, “could”, or “should” occur. Both Zimtu and Interra Copper caution readers and investors that any forward-looking information provided herein is not a guarantee of future results or performance and that actual results may differ materially from those in the forward-looking information due to various factors. Readers are referred to Interra Copper public filings for a more comprehensive discussion of potential risk factors and their potential effects, which may be accessed through its profile on appropriate regulatory websites.
Please read the full disclaimer within the entirety of this content, as fundamental risks and conflicts of interest exist. The author of this article has been compensated by Zimtu for the preparation, publication, and distribution of this content. Zimtu has been paid by Interra Copper for various services, including the distribution of this article. Note that Zimtu likely holds a financial interest related to Interra Copper and will profit from volume and price appreciation. Readers and investors are advised to conduct their own independent research and due diligence before making any investment decisions related to the content of this article.